1) DISTINCTION OF SHIPPING DOCUMENTS
Shipping documents are divided into below primary and secondary documents:
A) Primary
- Commercial invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of lading (ship-truck-airplane-railway)
- Insurance certificate
- Production certificate
- Certificate of circulation
B) Secondary
- Consular invoice
- Health certificate
- Plant certificate
- Certificate of analysis
- Weight certificate
USE OF SHIPPING DOCUMENTS
- Protection of the importer-carrier-exporter.
- Compliance of state and special requirements.
- They are means of settling payments and transferring holdings and are necessary for the entry or exit of goods through import and export customs.
2) PAYMENT METHODS
Settlement means that commercial payment of the goods’ value will go through a bank to the seller according to the agreed payment terms. The commercial payment of the goods’ value can be made in the following ways:
Α) In Cash (Cash Against Documents CAD)
Β) Credit (Days of Acceptance-D/A)
C) Credit Guarantee (Documentary Letter of Credit-L/C)
D) Advance Payment
Ε) Combined (Combination of above mentioned)
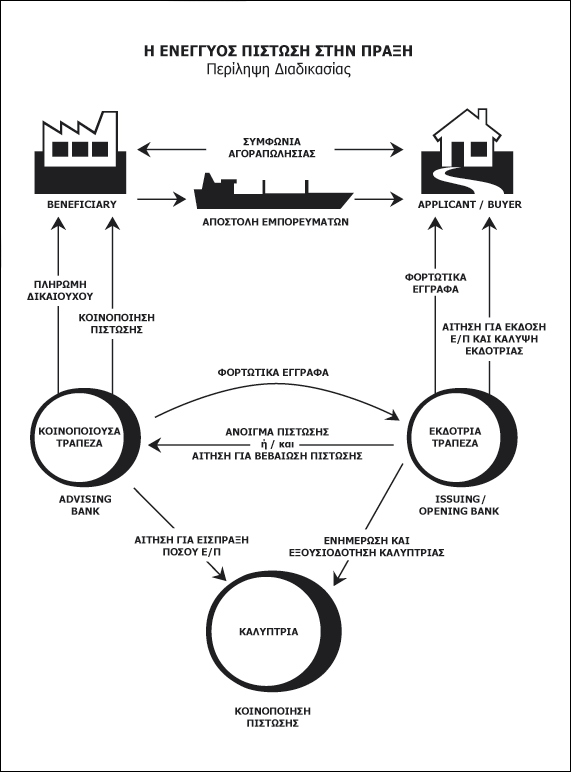
3) CREDIT GUARANTEE
A credit guarantee is an undertaking by a bank to pay the beneficiary of the credit, when he presents the required documents and as provided by the credit. To be more clear, we quote the definition given by the International Chamber of Commerce in the Uniform Rules and Customs (version 400/1984).
CREDIT means any agreement, however named or characterized, under which the bank (the issuing bank), which acts at the request and on the instructions of its customer (the principal of the credit).
The bank undertakes the obligation to make a payment to a third party (beneficiary) or at his order, to pay or accept bills of exchange (drafts), which have been issued by the beneficiary, or authorizes another bank to make such payment or to pay, accept or negotiate such bills of exchange (drafts), on receipt of the requested documents, and provided that they have been complied with credit terms.